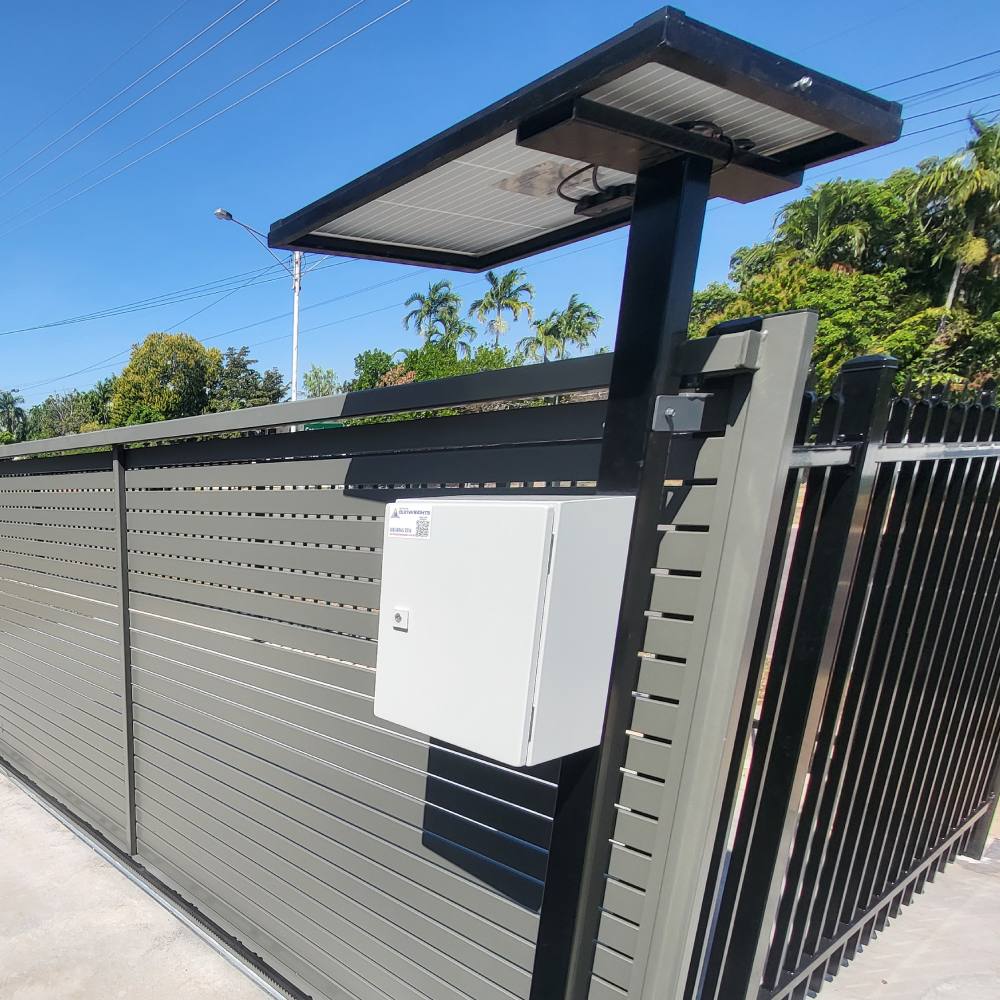
Duntech Ultimate: System Engineering Eliminates Compatibility Risks
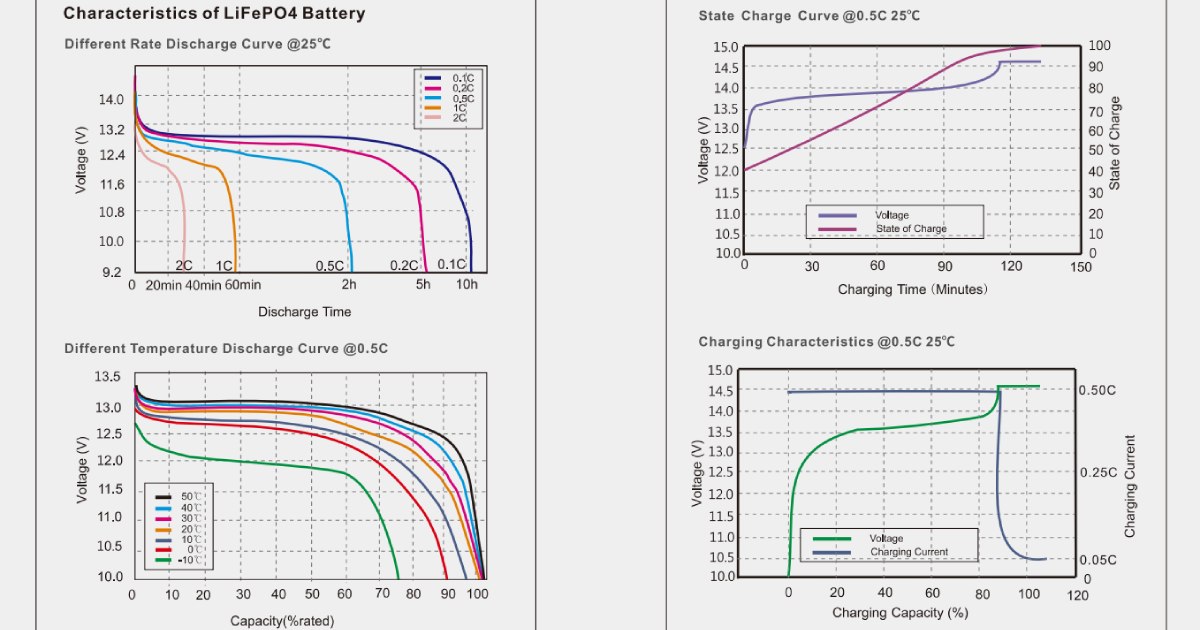
The technical advantages of LiFePO4 batteries mean nothing if the battery isn’t properly integrated into your gate motor system. This is the critical failure point where many people encounter problems – they buy a quality LiFePO4 battery, connect it to a gate motor system designed for lead-acid, and wonder why performance disappoints or why the expensive battery fails prematurely. The charging algorithm requirements for LiFePO4 batteries differ fundamentally from lead-acid. Lead-acid charging uses a three-stage profile: bulk charging at high current until voltage reaches a set point, absorption charging at constant voltage until current tapers, then indefinite float charging at reduced voltage. LiFePO4 needs constant-current charging until voltage reaches a set point, then constant-voltage charging until current drops below a threshold, with no float charging stage. The voltage set points differ too – lead-acid typically charges to 14.4-14.7V, while LiFePO4 charges to 14.2-14.6V depending on the specific cells used. Connect



